What is the difference between an X-Ray, CT scan, and MRI?
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

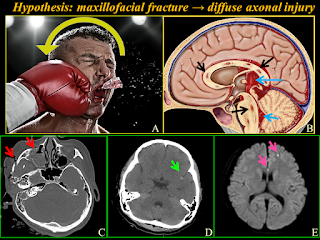
X-Ray, CT (Computed Tomography) scan, and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) are medical imaging techniques used to visualize internal structures of the body. Each modality has its strengths, limitations, and specific uses.
X-Ray
1. Principle: Uses ionizing radiation (X-rays) to produce images of internal structures.
2. Uses: Diagnoses bone fractures, lung diseases (e.g., pneumonia), and foreign objects in the body.
3. Limitations: Limited soft tissue contrast, cannot image internal organs clearly.
CT Scan
1. Principle: Combines X-ray images taken from different angles to produce cross-sectional images.
2. Uses: Diagnoses a wide range of conditions, including injuries, cancers, and vascular diseases.
3. Limitations: Involves higher radiation doses than X-rays, may not provide detailed images of soft tissues.
MRI
1. Principle: Uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of internal structures.
2. Uses: Diagnoses conditions affecting soft tissues, such as joints, muscles, and organs (e.g., brain, liver).
3. Limitations: May not be suitable for patients with metal implants, claustrophobia, or certain medical conditions.
In summary:
- X-Ray: Best for bone imaging and lung diseases.
- CT Scan: Ideal for diagnosing a wide range of conditions, especially those affecting internal organs.
- MRI: Excellent for imaging soft tissues, such as joints, muscles, and organs.
Your healthcare provider will determine the most suitable imaging modality based on your specific condition and medical history.
All reactions:
287287- Get link
- X
- Other Apps



Comments
Post a Comment